Deadly ‘Eye-Bleeding Disease’ Outbreak Takes Eight Lives!
Tanzania’s worldwide fitness management is running quickly to comprise a deadly virus; this is just like Ebola. The Kagera location in northern Japan has already stated 8 of 9 suspected cases of the Marburg virus, which is notorious for its high loss of life fee and severe signs.

The Marburg virus: What Is It?
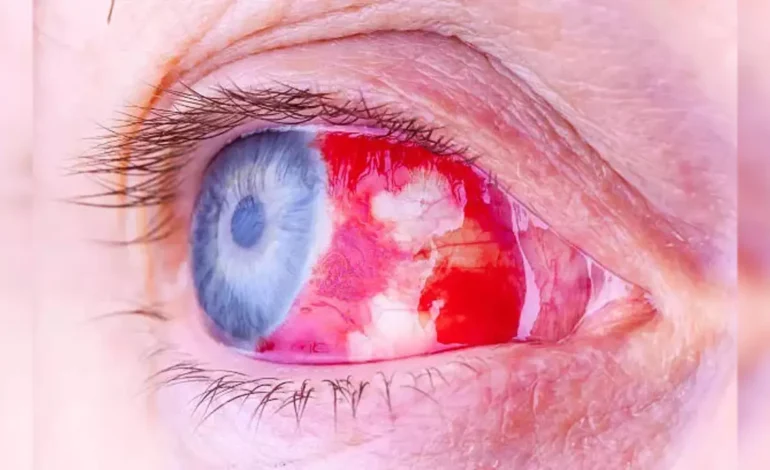
With a fatality price of as much as 88%, Marburg is one of the deadliest acknowledged viruses. Hemorrhagic fever, which is delivered on through the virus, can bring about internal bleeding in addition to, in intense instances, bleeding from the lips, ears, and eyes. Fever, vomiting, diarrhoea, and the surprising onset of complications are a number of the signs and symptoms, which get worse because the contamination worsens.
Marburg-inflamed sufferers regularly have “ghost-like” capabilities, such as an expressionless visage and deep-set eyes. Unfortunately, there aren’t any treatments or vaccinations for this lethal virus.

Current Situation in Tanzania
Place of Outbreak: All instances have been suggested in the Kagera area, in particular Biharamulo and Muleba districts.
Casualties: nine suspected cases, with 8 deaths confirmed to this point.
Reaction: the World Health Organisation (WHO) has dispatched emergency teams to the vicinity to reinforce surveillance and incorporate the outbreak.
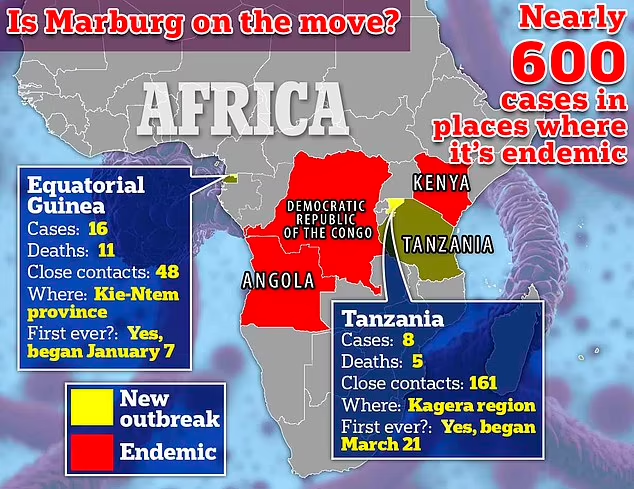
Regional Threat
Due to Kagera’s role as a transit hub, neighbouring international locations like Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo are on excessive alert. WHO warns that cross-border actions can also facilitate the virus’s unfold, despite the fact that Marburg isn’t always easily transmissible without direct contact with bodily fluids.

A Grim History
Tanzania has already encountered Marburg. A comparable outbreak that killed six humans over two months occurred in the Bukoba district in March 2023. Within the latest warfare towards the virus, neighbouring Rwanda reported 15 deaths out of sixty-six cases, most of which had been healthcare workers.

What You Need to Know?
Transmission: Marburg spreads through contact with the physical fluids of infected people, infected surfaces, or animals, mainly fruit bats.
chance to medical experts: Frontline medics are in particular prone because of close contact with patients.
global impact: while local chance is high, WHO assesses the global threat as low due to the fact the virus requires direct touch for transmission.

What’s Next?
WHO expects extra cases as surveillance efforts intensify. The source of the outbreak stays unknown, including the urgency of ongoing investigations.
Healthcare experts and contributors of the public in impacted regions are being cautioned via authorities to workout warning. Strict attention to contamination control protocols and activation of isolation of suspected instances are critical in warding off comparable activities.
Hold checking back for updates because the state of affairs unfolds.